NBIX is a biopharmaceutical company focused on discovering, developing and marketing of pharmaceuticals for the treatment of neurological, endocrine and psychiatric-based diseases and disorders.
Pipline
Its product pipeline includes INGREZZA (valbenazine), which provides a once-daily dosing treatment option for tardive dyskinesia; ONGENTYS (opicapone) is an adjunctive therapy to levodopa/carbidopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease; ORILISSA (elagolix) is used for the management of moderate to severe endometriosis pain in women, and ORIAHNN (elagolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate and elagolix capsules) is a non-surgical, oral medication option for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in women. Overall 12 Programs Currently in Mid- to Late-Stage Studies and Multiple Registrational & Phase 2 Study Readouts
Q4 2022 and FY Highlights
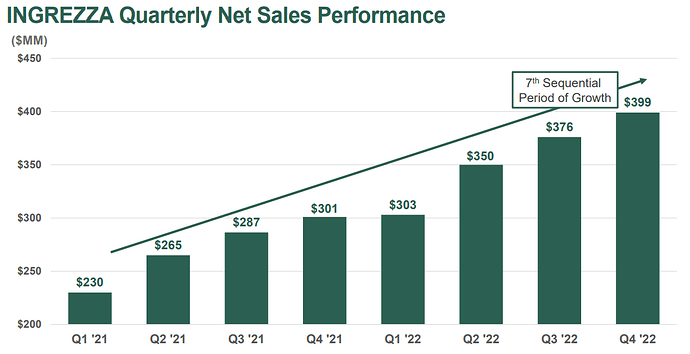
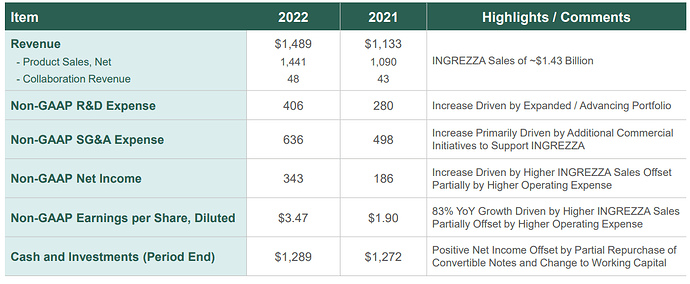
- INGREZZA® (valbenazine) Net Product Sales of over $1.4B with ~ 260,000 TRx in 2022

- Completed Expansion of Dedicated Psychiatry, Neurology and Long-Term Care Salesforce (Q2)
- Initiated Phase 2 Study of NBI-1117568, a Selective M4 agonist, for the Treatment of Schizophrenia (Q3)
- Initiated Phase 1 Study of NBI-1070770 (NCE) for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (Q3)
- Acquired Diurnal Group to Accelerate Establishment of Clinical Development and Commercial Capabilities in the U.K. (Q4)
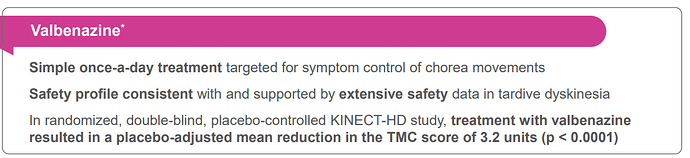
- sNDA of Valbenazine for the Treatment of Chorea Associated with Huntington Disease Accepted by the FDA (Dec)
Upcoming Catalyst (2023)
- Valbenazine - (KINECT-HD): PDUFA date for August 20, 2023.
https://neurocrine.gcs-web.com/news-releases/news-release-details/neurocrine-biosciences-presents-phase-3-data-kinect-hd-study
- Valbenazine Met the Primary Endpoint of Significant (p<0.0001) Improvement in Chorea Severity versus Placebo as Measured by the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS®) Total Maximal Chorea (TMC) Score, with Improvements Beginning in Week 2
- Clinically Meaningful Results, Demonstrated by Greater Response Rates, Seen by Clinicians (CGI-C) and Patients (PGI-C) for Valbenazine versus Placebo
- Valbenazine Safety Profile was Consistent with the Known Safety Profile
-
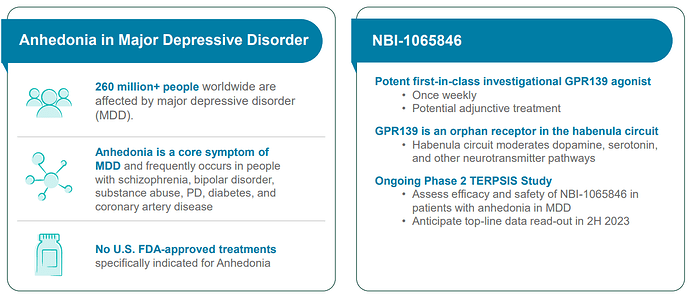
TAK-041 / NBI-1065846: Anhedonia in depression - Phase 2 topline data due in 2H 2023.
-
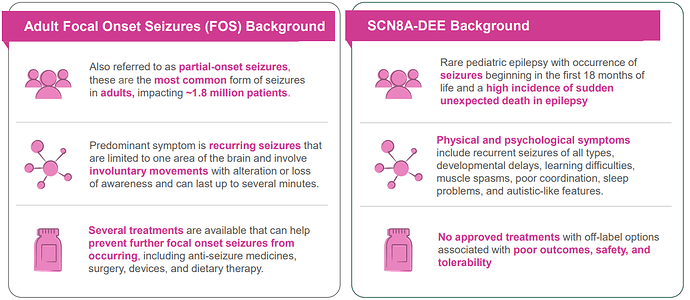
NBI-921352: SCN8A developmental and Focal Onset Seizure in Adults - Phase 2 data due 2H 2023
-
Crinecerfont - (CAHtalyst): Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) - adults and Pediatric - Phase 3 top-line data due in 2H 2023
Other Catalyst (2024)
- Valbenazine: Dyskinesia Due to Cerebral Palsy (DCP) - Phase 3 top-line data due in 2024
- Valbenazine: Schizophrenia - Phase 3 top-line data due in 2024.
Financials
~$1.3B Cash and Investments (as of 12/31/2022)
2023 Annual Net Sales Guidance of $1.67B to $1.77B
Position: Shares (announced in the Position System)
Huntington pathophysiology
Huntington’s disease, or HD, is caused by the expansion of a CAG trinucleotide repeat in the huntingtin gene on chromosome 4. This leads to the production of a toxic protein that accumulates in the brain, causing a progressive and, eventually, deadly loss of cognitive and motor function, including chorea. Chorea is a movement disorder that is characterized by rapid, irregular, and unpredictable movements, particularly in the basal ganglia, which plays a crucial role in movement control.
Huntington treatments
Unfortunately, there is no cure for Huntington’s disease, and treatment options are limited to symptom management. This includes medication for chorea control, cognitive and behavioral therapies for cognitive decline, and creating a calm and structured environment. The presence and severity of chorea should be evaluated to determine if treatment is necessary. VMAT2 inhibitors, such as tetrabenazine and Austedo, are typically the first-line therapy for most HD patients with interfering chorea, with Ingrezza expected to achieve FDA-approval later this year. Although VMAT2 inhibitors can cause reversible parkinsonism, they have a lower risk of tardive dyskinesia compared to antipsychotics. For HD patients with depression, agitation, or psychosis, a second-generation antipsychotic drug is usually the first-line therapy.